Catalog Number|Packaging
Mat. No |
Ref. No |
No. of preps |
-
Description
Exome sequencing provides a cost-effective alternative to whole genome sequencing, as it targets only the protein coding region of the human genome responsible for a majority of known disease-related variants, which is mainly related to diseases, cancers, population evolution, etc. Compared with the whole exome sequencing, the WGS has the features of high cost performance, high depth and high precision, and is more flexible and extensive in application.
-
Technical Workflow
Scheme design → Sample processing → Exon capture and library construction → Next generation sequencing → Data analysis → After-sales service
-
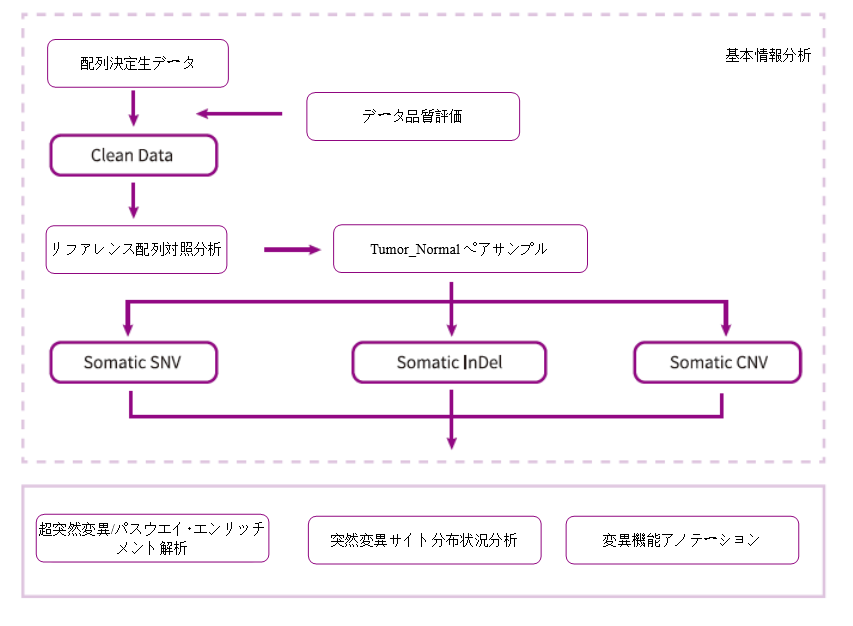
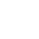
Analysis Workflow
-
Features
1. The protein coding sequence can be directly sequenced to find out the variation that affects the protein structure;
2. The sequencing depth is so high that common variation, low frequency variation and rare variation are discoverable;
3. Sequencing the exome region, accounting for about 1% of the genome, can effectively reduce the cost, cycle and workload.
-
Parameter
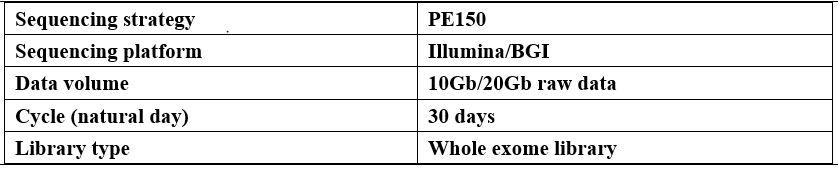
-
Applications
Pathogenesis, Genetic mechanism, biomarkers, Cancer research
-
Requirements of Samples
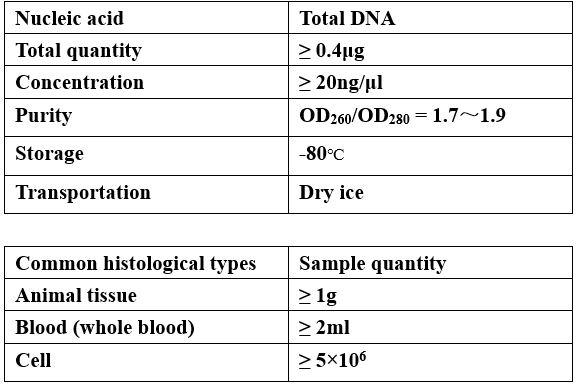
-
Results Demo
Distribution of sequencing depth and coverage

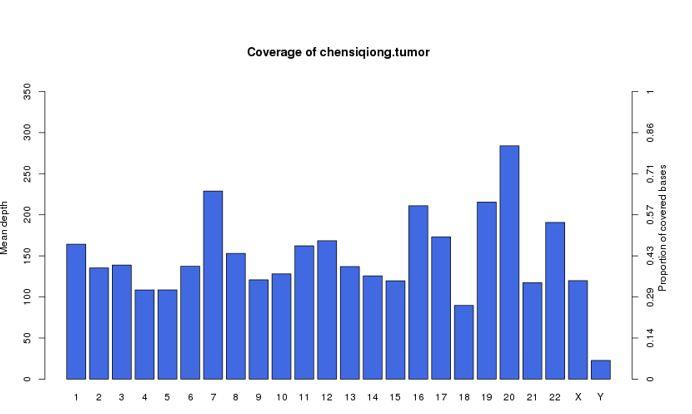
We use the comparison results after repeated marking to make statistics on coverage and depth. Generally, the sequencing reads of human samples can reach a comparison rate of over 95%; When the base coverage depth (read depth) of a site reaches over 10 X, the SNP detected at that site is considered to be more reliable.
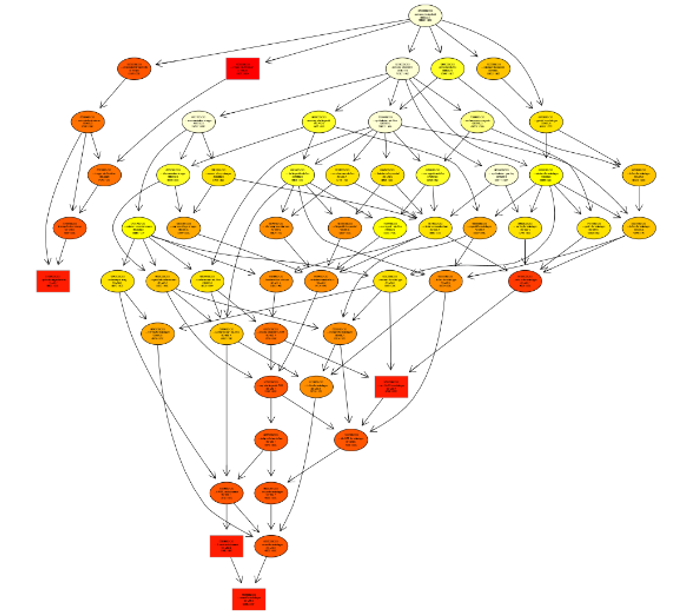
Characteristicsof genomic SNV

Somatic mutation, especially driver mutation, plays an important role in explaining the occurrence and progression of tumors. On the other hand, the generation of tumor drug resistance is also related to somatic mutation. Hence somatic mutation is the focus of cancer genome research, and it also distinguishes tumor genome research from disease research.
Functional enrichment analysis of variant genes
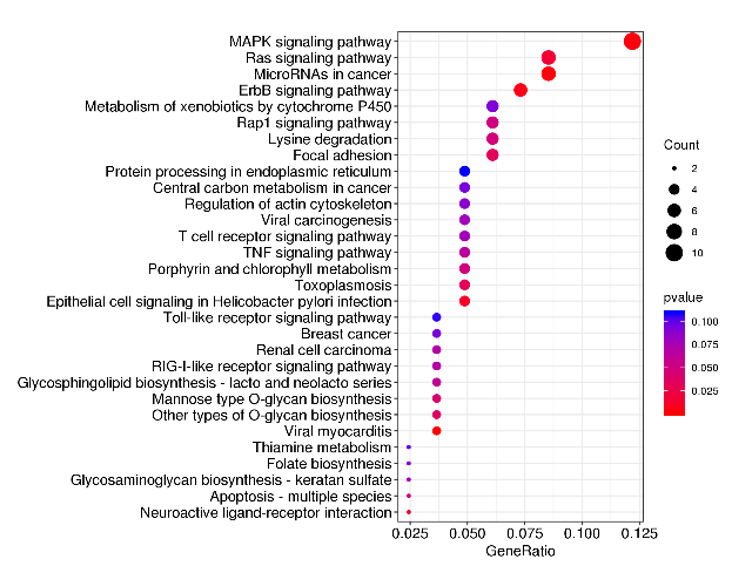
-
Sort by
-
Date
Date(
)
Date
Date(
)
Impact Factor
IF(
)
Impact Factor
IF(
)



 Inquire
Inquire