Catalog Number|Packaging
Mat. No |
Ref. No |
No. of preps |
|
4992259 |
GNG101-01 | 24 rxn |
|
4992260 |
GNG101-02 | 96 rxn |
-
Features
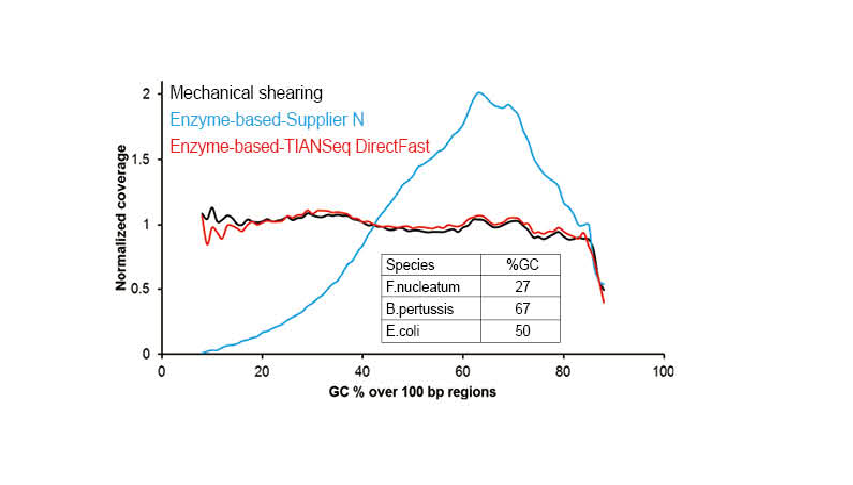
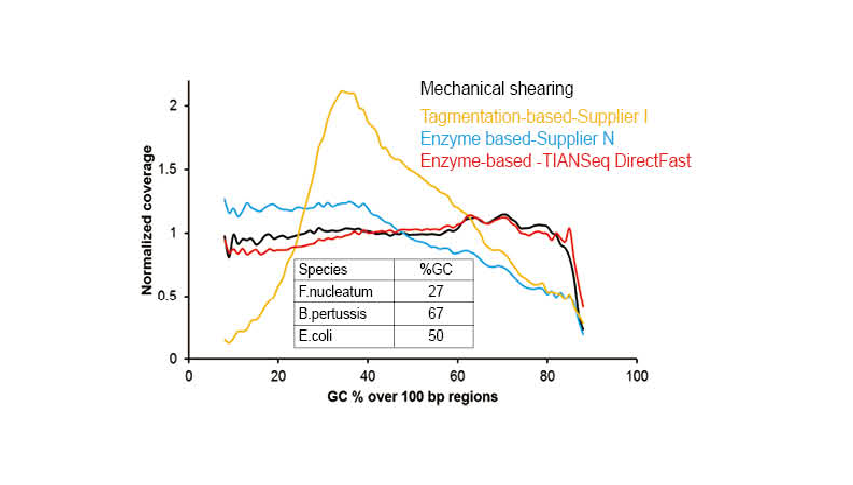
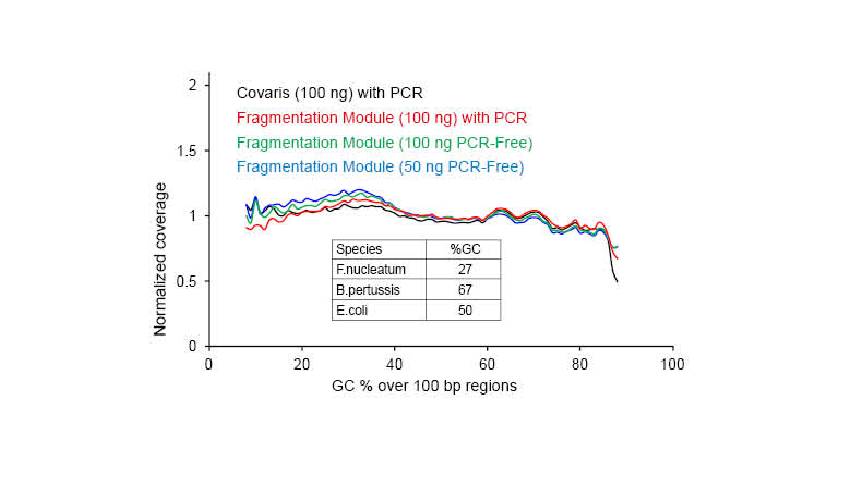
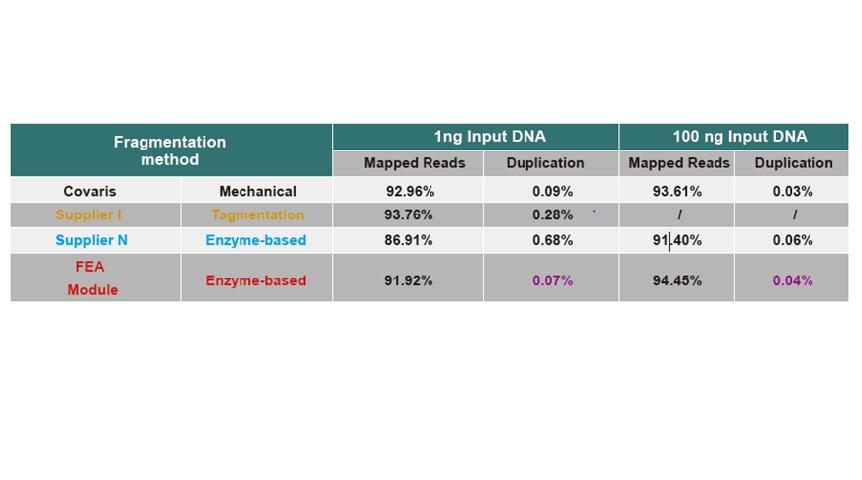
● No base bias of the DNA fragmentation process and PCR amplification process. Good sequencing uniformity.
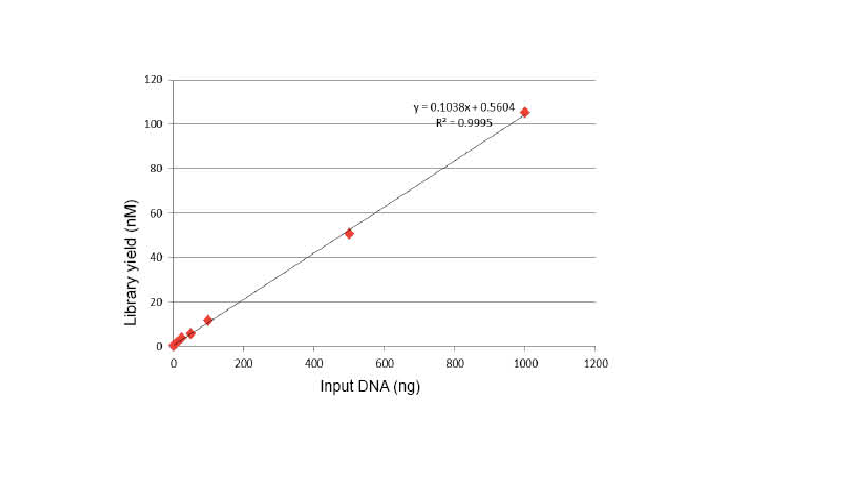
● High library conversion efficiency, and the DNA sample input can be as low as 1 ng.
● The one-tube enzymatic reaction is simple and convenient to operate, which does not need multi-step purification steps. The whole library construction process only needs 2.5 hours.
-
Description
The TIANSeq DirectFast Library Kit (illumina) is a DNA library construction kit specially optimized for illumina high-throughput sequencing platform. The kit is designed to perform DNA fragmentation, end repair and 3'-end dA-tailing in one step within a single tube. The product after this step can be directly used for adapter ligation without additional purification step. In addition, the PCR amplification reagent in this kit has been specially optimized to ensure high yield, good fidelity and no base preference for the amplified DNA library. The one-step streamline workflow of this kit skips multiple purification steps, and make sure the entire library construction process can be performed in 2.5 hr. This kit can achieve higher library construction efficiency, and can ensure the high efficiency of library construction for low input DNA samples.
-
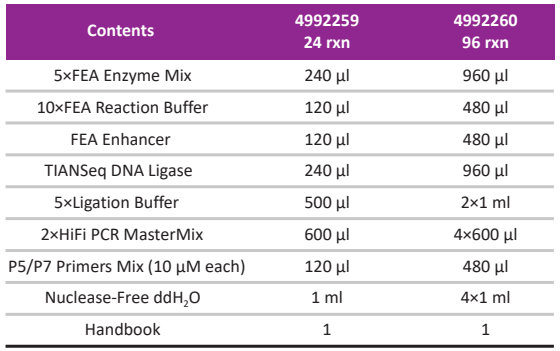
Kit Contents
-
Applications
Ideal choice for the DNA library construction for illumina high-throughput sequencing platform. -
Sample Input
1 ng~1 μg DNA. -
Required Reagents
● TIANSeq Single-Index Adapter (illumina) (Cat# 4992641/4992642/4992378)
● TIANSeq Size Selection DNA Beads (Cat# 4992358/4992359/4992979)
-
Storage Condition
The kit should be stored at -30~-15°C. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. The shelf life is one year. -
Product Highlights
● No base preference in the process of DNA fragmentation and PCR amplification, and the sequencing uniformity is ensured.
● High library construction efficiency can be achieved even with the DNA input as low as 1 ng.
● The easily performed one-tube enzymatic reaction skips multiple purification steps, and shortens the entire library construction process to only 2.5 hr.
-
Precautions
● Attention should be paid in the operating process to avoid cross-contamination between nucleic acid samples and products.
● Please use RNase- or DNase-free pipette tips or EP tubes for the experiments.
● Before starting, wipe down work area with RNase and DNase cleaning reagents such as RNase Away (Molecular BioProducts, Inc). Make sure there is no contamination of RNase and DNase.
● Before the library amplification, make sure the thermal cycler is calibrated and in a stable state.
● Please read the protocol carefully before the experiment. If test suspension is needed or the downstream test is not needed to be carried out immediately, the test products can be frozen and stored at -20°C and the subsequent test can be planned accordingly.
● Enzyme-based DNA fragmentation is sensitive to many factors, such as reaction temperature, reaction time, setup conditions, as well as the input DNA amount. It is highly recommended that users practice the experiment according to the steps and the optimized reaction parameters (such as reaction time) described in the protocol.
Experimental Example
Flexible sample input and fragmented size
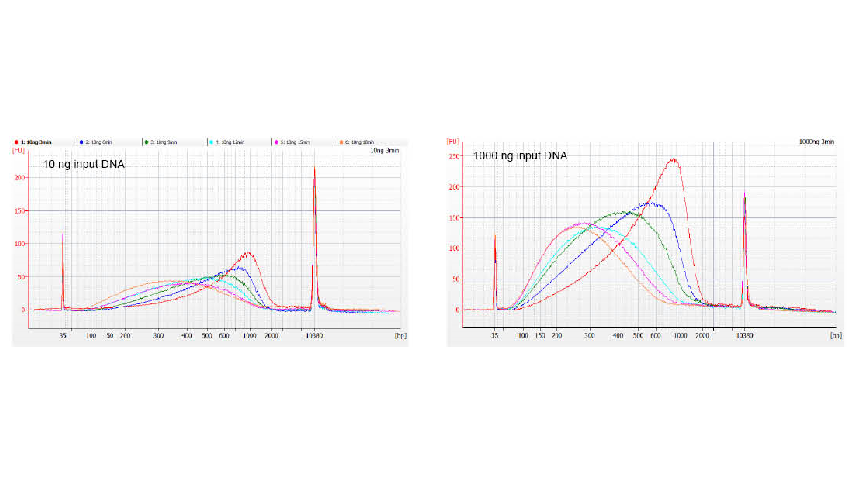
Figure 1. DNA fragmentation profiles of different reaction time. 10 ng and 1000 ng DNA were fragmented using TIANSeq DirectFast DNA Library Kit. The reaction products treated with different reaction time were purified by 1.8× Ampure XP magnetic beads and analyzed by Angilent 2100.
-
Sort by
-
Date
Date(
)
Date
Date(
)
Impact Factor
IF(
)
Impact Factor
IF(
)



 Inquire
Inquire