-
Storage
Room temperature (15-25℃ ) -
Description
Phase Lock Gel (PLG) is a patented gel prepacked in various sizes of centrifuge tubes. Under the centrifugal force, it forms a dense solid phase between the organic phase and the water phase due to the density difference. The layer acts as an effective barrier to protect nucleic acids from organic contamination. All the water phase can be easily pipetted out or poured out , so as to improve the nucleic acid recovery rate without the mixing of impurities and the accidental leaking of toxic phenol/ chloroform.
-
Features
■ Completely avoid the organic phase contamination, effectively improve the purity of nucleic acids.
■ Easy to pour out, and shorten the operation time.
■ All supernatant can be poured out clearly, and the nucleic acid recovery efficiency can be increased by 30%.
■ Effectively avoid exposure of laboratory personnel to toxic organic reagents.
■ Compatible with reagents and kits for various phenolic chloroform extraction methods.
-
Selection Guide
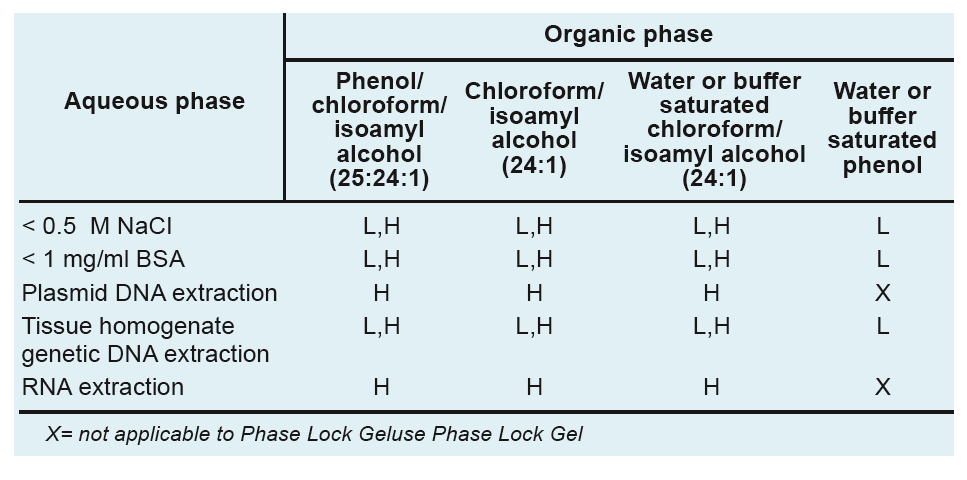
PLG has two densities, Heavy (H) and Light (L), which are suitable for any pure phenol, phenol/chloroform and chloroform extractions. The former is suitable for the extraction of plasmids, RNA and other samples containing high impurities (viscous) (not suitable for pure phenol extraction). The latter is suitable for restriction enzymatic digestion, cDNA synthesis, labeling reaction and conventional tissue gene DNA extraction (except for rat tail). The methods can also be selected by the compatibility formula of aqueous phase and organic phase, as listed in the following table.
-
Sort by
-
Date
Date(
)
Date
Date(
)
Impact Factor
IF(
)
Impact Factor
IF(
)


 Inquire
Inquire